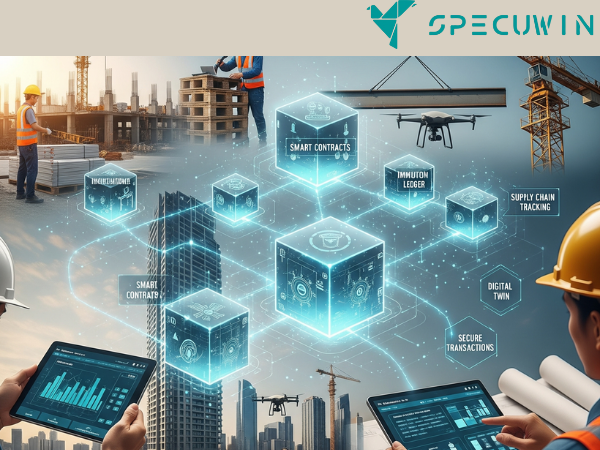
In an industry often criticized for its fragmentation, lack of transparency, and persistent project delays, the convergence of technologies offers a beacon of change. The Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) sector is on the cusp of a digital revolution, with blockchain emerging as a powerful catalyst. When combined with Building Information Modeling (BIM), this technology has the potential to redefine how projects are managed, data is shared, and trust is established among all stakeholders. This article delves into how blockchain can serve as the immutable backbone for modern AEC workflows, providing unprecedented transparency and efficiency, especially through its synergy with BIM.

The Trust Deficit in Traditional AEC Projects
Traditional construction projects are a web of complex interactions involving multiple parties, including clients, architects, engineers, contractors, and suppliers. The reliance on paper-based contracts and centralized data systems creates significant vulnerabilities. Disputes over payments, change orders, and material provenance are common, leading to cost overruns and project delays.
The lack of a single, reliable source of truth means that information is often siloed and prone to manipulation. This not only erodes trust but also makes it challenging to ensure accountability. For instance, verifying a material’s origin or an asset’s maintenance history can be a convoluted process, creating opportunities for fraud and non-compliance. Blockchain addresses this fundamental problem by creating a decentralized, tamper-proof digital ledger that records every transaction and piece of data in real-time, making it accessible and verifiable for all authorized parties.
Read more on:- The Value of BIM Outsourcing for Architectural and Engineering Firms
The Foundational Role of Blockchain Technology
At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that records transactions in “blocks” linked by cryptographic hashes. Each new block contains a unique hash that references the previous block, creating an unbreakable chain of data. This immutable nature is the source of its immense power.
In the context of the AEC industry, this means:
- Immutability: Once a transaction be it a payment, a document approval, or a design change is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted. This creates an unchangeable record of all project activities, serving as a reliable audit trail and reducing disputes.
- Transparency: Every participant on the network has access to the same shared ledger, providing a single, trustworthy source of information. This transparency fosters accountability and enables real-time project monitoring.
- Decentralization: The data is not stored on a single, vulnerable server. It is replicated across a network of computers, meaning there is no central point of failure. This enhances security and resilience against cyber-attacks.
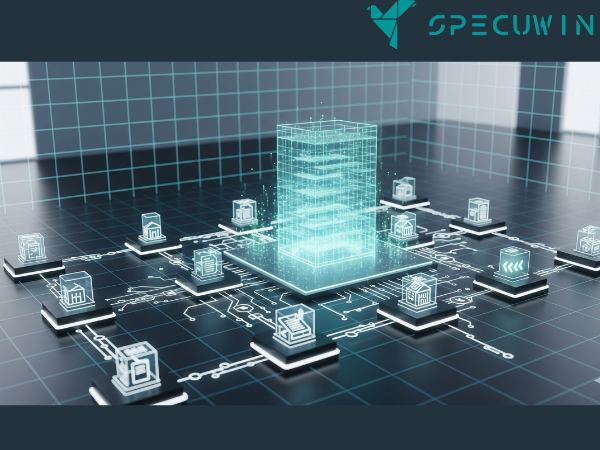

Synergy of Blockchain and BIM for Enhanced Workflows
While blockchain provides the immutable ledger, BIM (Building Information Modeling) provides the rich, data-centric model of a construction project. BIM creates a digital representation of a building, capturing all its physical and functional characteristics. The real magic happens when these two technologies are integrated.
BIM integration with blockchain allows for:
- Secure Data Management: All changes and updates to a BIM model can be recorded on the blockchain. This creates a secure, immutable history of the model’s evolution, preventing unauthorized modifications and ensuring data integrity.
- Improved Collaboration: With a shared BIM model on a blockchain, architects, engineers, and contractors can collaborate with confidence, knowing that they are working with the most current and verified information. This reduces errors and improves overall project coordination.
- Streamlined Asset Management: The final BIM model can be transferred to the building owner, along with the blockchain record of its entire lifecycle. This includes everything from material certifications to maintenance logs, which is a powerful tool for facility management.
Read more on:- Why BIM is a Crucial Skill for a Future-Ready Career in AEC
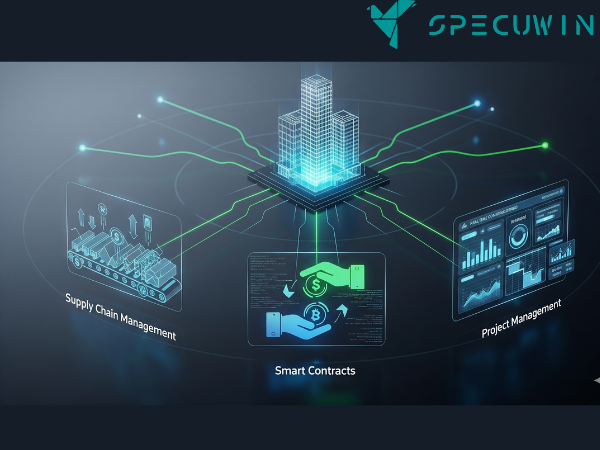
Key Applications of Blockchain in Construction Workflows
Supply Chain Management
The construction supply chain is notoriously complex. Blockchain can track materials from their origin to the construction site, providing a transparent and verifiable record of their quality, ethical sourcing, and delivery status. This not only helps combat the use of counterfeit materials but also simplifies compliance and auditing processes. An example is the use of IoT sensors on materials that automatically update the blockchain ledger upon arrival at a site, creating a real-time, verifiable record.
Smart Contracts for Automated Payments
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms of the contract written directly into code. They can automate tasks like payments and compliance checks when predefined conditions are met. For example, a smart contract could release a payment to a subcontractor as soon as a project milestone, verifiable through BIM data on the blockchain, is completed. This reduces administrative overhead, minimizes disputes, and speeds up the payment process, which is a major pain point in the industry.
Enhanced Project Management and Accountability
By creating a secure, shared platform, blockchain enhances project management by giving all stakeholders real-time access to immutable project data. This transparency helps project managers track progress, identify potential delays early, and improve communication. With a clear record of actions and responsibilities, blockchain holds all parties accountable, leading to more efficient and well-managed projects.
FAQ’s
1. What is the main benefit of using blockchain in construction?
A. The main benefit is creating a secure and transparent record of all project transactions and data. This enhances trust, reduces fraud, and improves efficiency by providing a single, immutable source of truth for all stakeholders.
2. How do smart contracts work in a construction project?
A. Smart contracts are self-executing digital contracts that automatically enforce terms when certain conditions are met. For instance, they can be programmed to release a payment to a subcontractor automatically once a project milestone, such as the completion of a foundation, is verified on the blockchain.
3. What is the connection between blockchain and BIM?
A. BIM provides the data-rich model of a building, and blockchain provides the secure, immutable ledger to record all changes and updates to that model. This integration ensures the integrity and reliability of the BIM data throughout the project lifecycle.
4. Is blockchain technology cost-effective for small construction firms?
A. While initial implementation costs can be a factor, blockchain can lead to significant long-term cost savings by reducing administrative overhead, minimizing disputes, and preventing delays caused by a lack of transparency or miscommunication. The cost of setting up a private blockchain for a business can vary based on specific needs.
5. What are the major challenges to adopting blockchain in the AEC industry?
A. Key challenges include the complexity of integrating blockchain with existing systems, the need for industry-wide standardization, and regulatory uncertainties. Educating stakeholders and addressing scalability and performance issues are also crucial for widespread adoption.
Read More On:-
For more information about engineering, architecture, and the building & construction sector, go through the posts related to the same topic on the Specuwin Blog Page.
Find out more accurately what we are going to take off in the course of applying leading new technologies and urban design at Specuwin.
