In a world increasingly focused on environmental responsibility, the construction industry is undergoing a monumental shift. What was once a niche movement a small, dedicated effort to be “green” is now a mainstream necessity. Welcome to the era of sustainable construction, a practice that’s reshaping how we build and interact with the world around us. This isn’t just a fleeting trend; it’s a commitment to building a better, healthier future.
But what does sustainable construction really mean on a practical level? It’s about more than just using eco-friendly materials. It’s a holistic approach that considers every phase of a building’s lifecycle, from the initial design and material sourcing to energy consumption and waste management. It’s about creating structures that are not only beautiful and functional but also kind to the planet and the people who inhabit them.
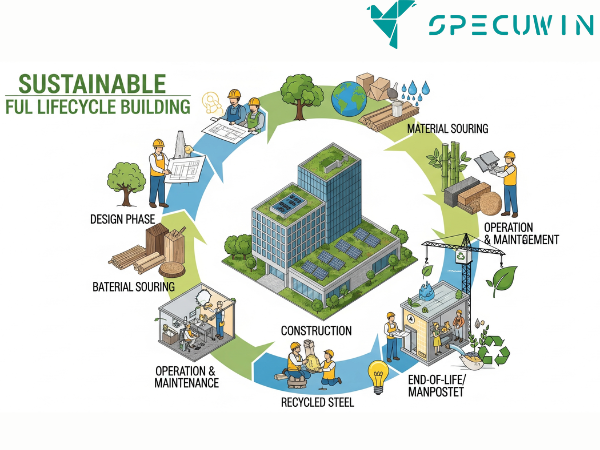
Why Sustainable Construction Matters: Beyond the Hype
The reasons for adopting sustainable practices go far beyond corporate social responsibility. They are rooted in tangible, long-term benefits environmental, economic, and social.
Read more on:- From risk to resilience how engineers are tackling climate change
Environmental Impact: Reducing Our Carbon Footprint
The construction industry is a major consumer of natural resources and a significant contributor to global carbon emissions. Sustainable construction aims to reverse this. By focusing on resource efficiency, waste reduction, and the use of renewable energy, we can dramatically lessen our ecological footprint. This includes everything from preserving ecosystems and conserving water to using low-impact materials and reducing the pollution caused by construction activities. The move towards more resilient infrastructure is also a critical part of this. To understand how engineering is tackling broader environmental challenges, you can read about how engineers are taking on climate change.
Read more on:- Green building in India components importance and a sustainable future
Economic Benefits: A Wise Investment for the Future
While the initial costs of a green building project may seem higher, the long-term economic benefits are undeniable. Sustainable buildings typically have lower operational and maintenance costs due to improved energy and water efficiency. They also often command higher property values and attract government incentives like tax credits and rebates. This makes a green building not just a feel-good project, but a smart financial decision with a high return on investment.
Social Well-being: Building for People
Sustainable buildings are designed with human health and comfort in mind. Features like improved indoor air quality (by using non-toxic materials), increased natural light, and access to green spaces contribute to the well-being and productivity of occupants. A building that breathes, that connects its inhabitants to nature, is a building that fosters a healthier and happier community.
The Blueprint for Green Building: Principles & Practices
Embracing sustainable construction requires a multi-faceted approach. Here are the core principles and practices that form the foundation of a truly green project.
1. Smart Site Selection and Design
The sustainability journey begins before a single brick is laid. This involves choosing a site that minimizes environmental impact, such as a brownfield (previously developed land) over a greenfield (undeveloped land). Design also plays a crucial role; passive solar design, for example, uses a building’s orientation and window placement to maximize natural light and reduce the need for artificial heating and cooling.

2. The Power of Green Materials: Building Blocks of a Better Future
The materials we use are perhaps the most visible aspect of sustainable construction. This is where innovation shines. Instead of relying on traditional, resource-intensive materials, builders are turning to a wide array of eco-friendly alternatives.
- Bamboo: A fast-growing grass with a strength-to-weight ratio comparable to steel. It’s an excellent, renewable alternative to traditional wood.
- Recycled Steel: Steel is one of the most recycled materials in the world. Using recycled steel reduces the need for new iron ore mining and saves a tremendous amount of energy.
- Hempcrete & Mycelium: These bio-based materials are created from natural sources like hemp stalks and fungi. They are lightweight, fire-resistant, and have a negative carbon footprint, as they absorb CO2 as they grow.
- Reclaimed Wood: Repurposing lumber from old buildings not only saves trees but also adds a unique character and history to a new structure.
- Rammed Earth & Cob: These ancient building techniques use locally sourced soil, sand, and clay to create durable, energy-efficient walls with minimal environmental impact.
Read more on:- Sustainable structures eco-friendly approaches in modern construction
3. Energy and Water Efficiency: The Core of Sustainability
A truly sustainable building is a lean, mean, resource-saving machine.
- Renewable Energy Integration: From solar panels on the roof to geothermal systems, buildings are being designed to generate their own power, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- High-Performance Insulation: Advanced insulation materials like aerogels or sheep’s wool minimize heat loss and gain, cutting down on heating and cooling demands.
- Water Conservation Systems: Rainwater harvesting, greywater recycling, and low-flow fixtures are becoming standard practice, drastically reducing water consumption.

4. The Digital Revolution: How Technology Fuels Green Building
Modern technology is the engine driving the sustainable construction movement.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM enables precise material planning and reduces on-site waste. By creating a digital twin of a building, architects and engineers can optimize every detail for sustainability before a single shovel hits the ground.
- Smart Building Technology: AI-powered sensors and smart thermostats monitor and adjust lighting, temperature, and ventilation in real-time, ensuring optimal energy use.
- 3D Printing & Modular Construction: These innovative methods reduce waste by creating components off-site in a controlled factory environment. This also increases efficiency and reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation.
The Challenges and How to Overcome Them:-
Despite the clear advantages, the path to widespread sustainable construction isn’t without its obstacles. Initial costs, a lack of awareness, and resistance to change can all be hurdles. However, the industry is overcoming these challenges through:
- Education: As more professionals become LEED or WELL certified, the knowledge and expertise for green building become more accessible.
- Governmental Support: Policies and incentives are making sustainable projects more financially viable.
- Innovation: The continuous development of new, affordable, and high-performance green materials is making sustainability an easy choice.
Key Takeaways: Starting Your Sustainable Journey:-
The transition to a greener building industry is not an overnight process, but it’s a journey worth taking. Whether you’re an architect, an engineer, a builder, or a homeowner, you have a role to play. By understanding the principles, embracing the innovations, and prioritizing a long-term vision, we can build a world that is more resilient, more beautiful, and more sustainable.
The future of construction is green. It’s a future where every structure tells a story of innovation, efficiency, and a deep respect for our planet.
FAQs:-
Q1: Is sustainable construction more expensive?
A: While the initial investment can sometimes be higher, sustainable buildings typically have lower long-term operational costs, making them a more cost-effective choice over their lifecycle. Government incentives and increasing material availability are also helping to close the cost gap.
Q2: How do green buildings improve indoor air quality?
A: Green buildings use non-toxic paints, adhesives, and materials that don’t release harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs). They also incorporate advanced ventilation systems to ensure a continuous supply of fresh, filtered air.
Q3: What are some examples of sustainable materials?
A: Common examples include bamboo, recycled steel, reclaimed wood, cork, straw bales, and bio-based materials like hempcrete and mycelium.
Q4: What is the difference between green building and sustainable construction?
A: The terms are often used interchangeably, but “green building” typically refers to the structure itself and its features (e.g., energy-efficient windows, solar panels), while “sustainable construction” encompasses the entire process, including site selection, material sourcing, and waste management.
Q5: What is a Net-Zero Energy Building?
A: A net-zero energy building is designed to produce as much energy as it consumes over the course of a year, often through a combination of energy-efficient design and on-site renewable energy generation.
Read More On:-
For more information about engineering, architecture, and the building & construction sector, go through the posts related to the same topic on the Specuwin Blog Page.
Find out more accurately what we are going to take off in the course of applying leading new technologies and urban design at Specuwin.
